Artificial Intelligence and Big Data
Postgraduate Program in Central Banking (CEMFI)
About this Course
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming economics and finance, from credit risk assessment to economic forecasting and policy analysis. Recent breakthroughs in machine learning and generative AI have opened unprecedented opportunities for researchers and practitioners to extract insights from vast datasets and automate complex analytical tasks.
This course provides a hands-on introduction to the AI techniques driving these changes. While we explore the theoretical foundations necessary to understand how these methods work, our primary focus is on practical implementation. You will learn to build, and train machine learning models using Python, the dominant language in AI and data science. Through a combination of conceptual understanding and applied programming, you will gain the skills needed to harness AI for tackling real-world problems in economics, finance, and beyond.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to:
- Understand core AI concepts: Grasp the fundamental principles behind supervised learning, natural language processing, and generative AI that drive modern applications in economics and finance
- Implement machine learning models: Build and train decision trees, neural networks, and other ML algorithms to solve prediction and classification problems using real-world datasets
- Process and analyze text data: Apply natural language processing techniques to extract insights from textual sources such as financial reports, news articles, and policy documents
- Leverage generative AI: Work with large language models (LLMs) programmatically through APIs, going beyond chatbot interactions to automate tasks and build AI-powered applications
- Use Python for data science: Write Python code using industry-standard libraries for data manipulation, visualization, and machine learning
Course Structure
This course is divided into four parts, each focusing on different aspects of AI and big data:
- Part I: Foundations
- Introduction to Artificial Intelligence and Big Data
- Introduction to Python
- Part II: Supervised Machine Learning
- Overview of Supervised Learning
- Decision Trees
- Neural Networks
- Practice Session I
- Part III: Natural Language Processing
- Overview of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Classical NLP Approaches
- Practice session II
- Part IV: Generative AI
- Overview of Generative AI
- Large Language Models (LLMs)
- Practice session III
Prerequisites
This course is designed to be accessible to students with diverse backgrounds. The following will help you get the most out of the course:
- Statistics and probability: A basic understanding of statistical concepts (mean, variance, distributions) and probability theory at the undergraduate level.
- Mathematics: Familiarity with linear algebra (vectors, matrices) and calculus (derivatives, gradients) will be helpful for understanding how machine learning algorithms work under the hood. However, we will try not to go too deeply into the mathematics. Instead, we focus on building intuition about how models work and on practical implementation.
The following is explicitly not required :
- Programming experience: Prior programming knowledge is helpful but not required. We introduce Python from the ground up in Part I, covering all necessary programming concepts for the course.
- Machine learning background: No prior experience with AI or machine learning is expected. We start with the fundamentals and build up to advanced topics.
Useful Resources
The course does not follow a particular textbook but has drawn material from several sources such as
- Hastie, Tibshirani, and Friedman (2009), “The Elements of Statistical Learning”
- Murphy (2012), “Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective”
- Murphy (2022), “Probabilistic Machine Learning: An Introduction”
- Murphy (2023), “Probabilistic Machine Learning: Advanced Topics”
- Goodfellow, Bengio, and Courville (2016), “Deep Learning”
- Bishop (2006), “Pattern Recognition And Machine Learning”
- Nielsen (2019), “Neural Networks and Deep Learning”
- Sutton and Barto (2018), “Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction”
Note that all of these books are officially available for free in the form of PDFs or online versions (see the links in the references). However, you are not required to read them and, as a word of warning, the books go much deeper into the mathematical theory behind the machine learning techniques than we will in this course. Nevertheless, you may find them useful if you want to learn more about the subject.
Regarding programming in Python, McKinney (2022) “Python for Data Analysis” might serve as a good reference book. The book is available for free online and covers a lot of the material we will be using in this course. You can find it here: Python for Data Analysis.
Software Installation Notes
In this course, we will use Nuvolos to run all Python code, which provides a pre-configured environment with all the necessary packages. If you would like to set up a local Python environment on your computer instead, you can use the following guide. We use the Anaconda distribution, which simplifies package management and ensures everyone has a consistent development environment. For code editing and running Jupyter notebooks, we use Visual Studio Code (VS Code), a powerful and beginner-friendly code editor.
The following instructions will guide you through installing Python, creating a dedicated environment for this course, and setting up VS Code on your machine.
Anaconda Installation
The first step is to install the Anaconda distribution:
Download the Anaconda distribution from anaconda.com. Note: If you are using a M1 Mac (or newer), you have to choose the 64-Bit (Apple silicon) Graphical Installer. With an older Intel Mac, you can choose the 64-Bit (Intel chip) Graphical Installer. With Windows, you can choose the 64-Bit Graphical Installer (i.e., the only Windows option).
Open the installer that you have downloaded in the previous step and follow the on-screen instructions.
If it asks you to update Anaconda Navigator at the end, you can click
Yes(to agree to the update),Yes(to quit Anaconda Navigator) and thenUpdate Now(to actually start the update).
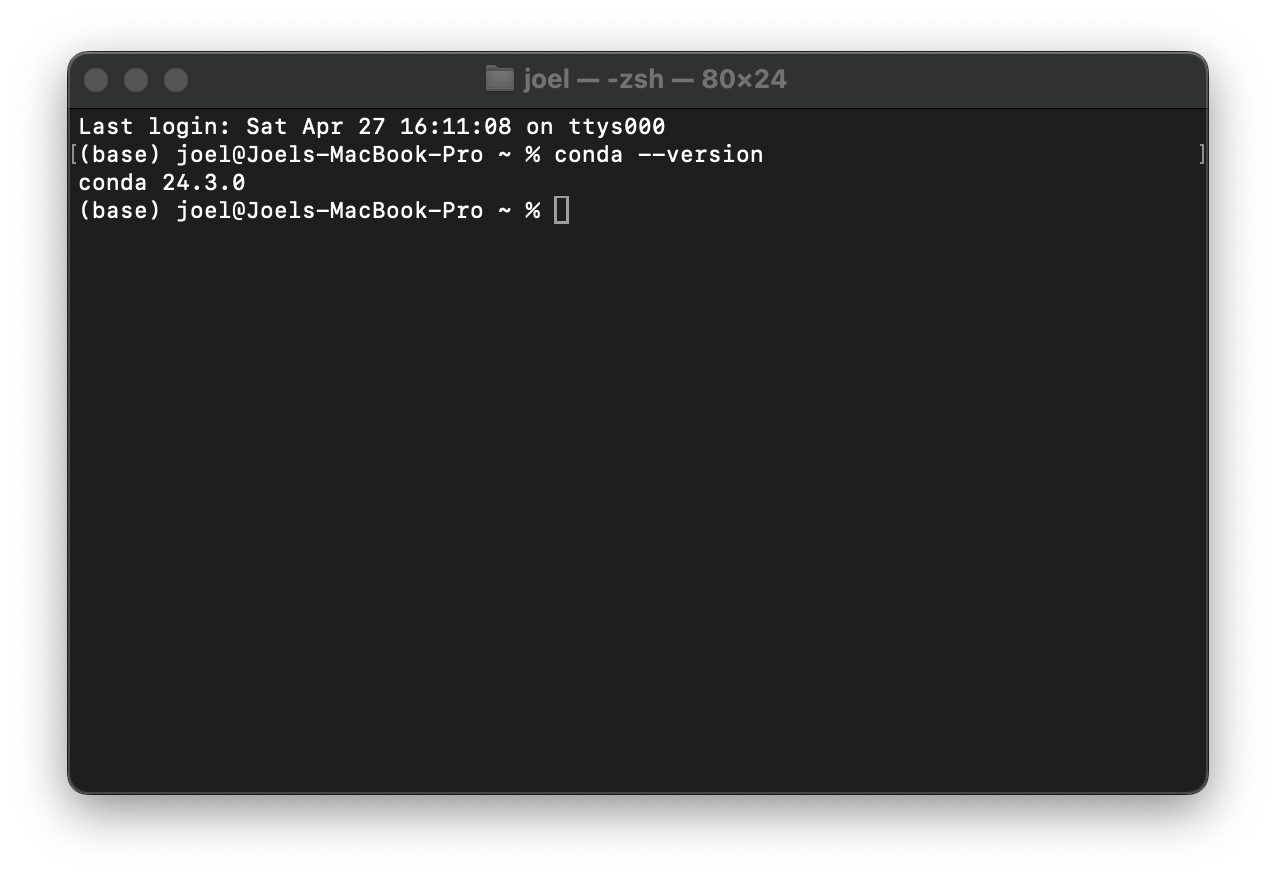
To confirm that the installation was successful, you can open a terminal window on macOS/Linux or an Anaconda Prompt if you are on Windows and run the following command:
conda --versionThis should display the version of Conda that you have installed. If you see an error message, the installation was likely not successful and you should ask for advice from your peers or send me an email.
Creating a Conda Environment
Next, we want to create a new environment for this course that contains the correct Python version and all the Python packages we need. We can do this by creating a new Conda environment from the environment.yml provided on Moodle.
Open a terminal window on macOS/Linux or an Anaconda Prompt if you are on Windows.
There are two ways to create the Conda environment:
Option A: Run the following command from the terminal or Anaconda Prompt:
conda env create -f https://aibigdata.joelmarbet.com/environment.ymlThis downloads the
environment.ymlfile automatically and creates the environment.Option B: Download the
environment.ymlfile manually:Navigate to the folder where you have downloaded the
environment.ymlfile. On macOS/Linux, you can do this by running the following command in the terminal:cd ~/Downloadswhich will navigate to the
Downloadsfolder in your home directory.On Windows, you can do this by running the following command in the Anaconda Prompt:
cd "%userprofile%/Downloads"which will navigate to the
Downloadsfolder in your user profile.Note that if you use a different path that contains space you need to put the path in quotes, e.g.,
cd "~/My Downloads".Create a new Conda environment from the
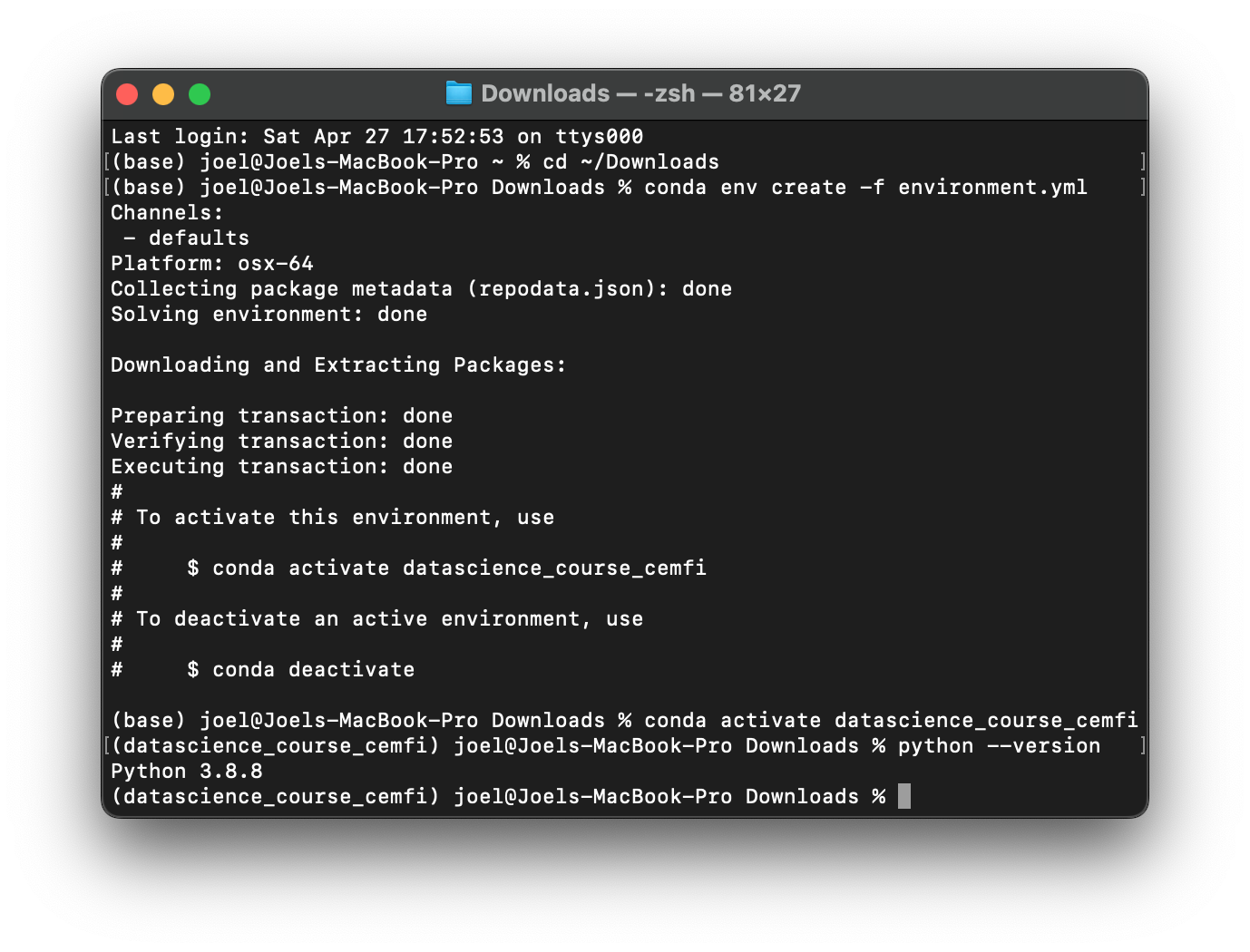
environment.ymlfile by running the following command in the terminal or Anaconda Prompt:conda env create -f environment.yml
Either option will create a new Conda environment called
ai-big-data-cemfiwith the correct Python version and all the Python packages we need for this course. Note that the installation might take a few minutes.Activate the new Conda environment by running the following command in the terminal or Anaconda Prompt:
conda activate ai-big-data-cemfi
To confirm that the environment was created successfully, you can run the following command in the terminal or Anaconda Prompt:
conda env listThis should display a list of all Conda environments on your machine, with an asterisk (*) next to the currently active environment. You should see ai-big-data-cemfi in the list.
If you accidentally make changes to the environment and want to reset it to the original state, you can do this by navigating to the folder where you have downloaded environment.yml and then running the following command in the terminal or Anaconda Prompt:
conda env update --file environment.yml --pruneAlternatively, you can also update the environment by running the following command in the terminal or Anaconda Prompt, which downloads the environment.yml file automatically from the course website:
conda env update --file https://aibigdata.joelmarbet.com/environment.yml --pruneThis can also be used to update the environment if we add new packages to the environment.yml file.
Installing VS Code
The last step is to install the Visual Studio Code (VS Code) editor:
- Download the Visual Studio Code editor from code.visualstudio.com.
- Open the installer that you have downloaded in the previous step and follow the on-screen instructions.
We also need to install some VS Code extensions that will help us with Python programming and Jupyter notebooks:
Open VS Code.
Click on the
Extensionsicon on the left sidebar (or pressCmd+Shift+Xon macOS orCtrl+Shift+Xon Windows).
Installing Extensions in VSCode Search for
Pythonand click on theInstallbutton for the extension that is provided by Microsoft.Search for
Jupyterand click on theInstallbutton for the extension that is provided by Microsoft.
Testing the Installation
To test the installation, you can download a Juypter notebook from Moodle and open it in VS Code:
Open the Jupyter notebook in VS Code.
Click on
Select Kernelin the top right corner of the notebook and choose theai-big-data-cemfikernel.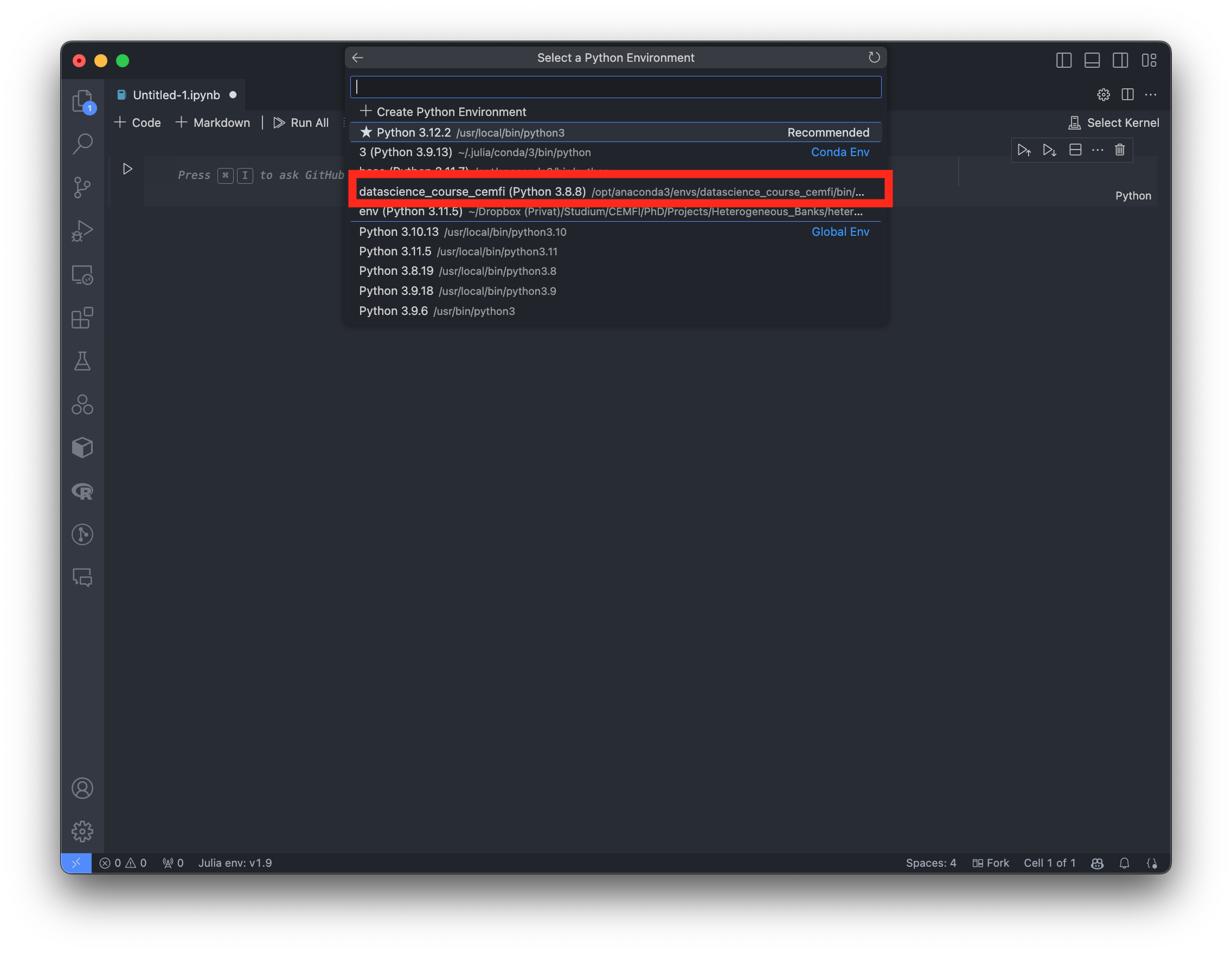
VSCode Jupyter Kernel Selection Run the first cell of the notebook by clicking on the
Execute Cellbutton next to the cell on the left.
If you see the output of the cell (or a green check mark below the cell), the installation was successful.
If you have issues running Jupyter notebooks in VSCode, you can also run them in the browser. To do this, you can open a terminal window on macOS/Linux or an Anaconda Prompt if you are on Windows and run the following command:
jupyter notebookThis will open a new tab in your default browser with the Jupyter notebook interface. You can then navigate to the folder where you have downloaded the course materials and open the notebooks from there.
